Minimum Requirements for Sisense in Linux Environments
Below are descriptions and explanations describing the minimum requirements for Sisense in Linux environments.
Supported Browsers
The Sisense Web Application runs in the following HTML5 supported browsers:
- Microsoft Edge
- Google Chrome
- Firefox
- Safari version 7 and higher - Sisense supports Safari 10 and higher when embedding iFrames.
Note:
If you are using Internet Explorer 11, Sisense recommends moving to another browser. Microsoft ended IE11 support for various Microsoft products during 2021 and Sisense stopped supporting IE11 by the end of 2021. IE11 is not supported for the Sisense internal web-based file browser application.
In order to display Sisense properly, the browser dimensions must be a minimum resolution of 1280px*800px.
The Sisense Web Application also works in mobile phone and tablet browsers that support HTML5. See Viewing Dashboards on Mobile Devices to learn more about mobile compatibility.
Minimum System Requirements
The Sisense Linux deployment is certified to run on the operating systems listed in the table below.
Note the following:
- Sisense only supports x86-64/AMD64 architectures, (for example, ARM64 is not currently supported). You can verify your architecture by
running the
hostnamectlcommand in Linux. - The OS versions specified below are also based on the minor release number, which should be taken into consideration to ensure proper compatibility. (For example, CentOS 8.4 is not currently supported.)
- The OS must be an official release of the given Linux OS, and one that has not been customized (for example, where the OS was modified to harden the kernel).
-
SELinux must be disabled on a host node(s), or set to Permissive mode, as Sisense components are managed by k8s on a security context. For more information, see Configure a Security Context for a Pod or Container.
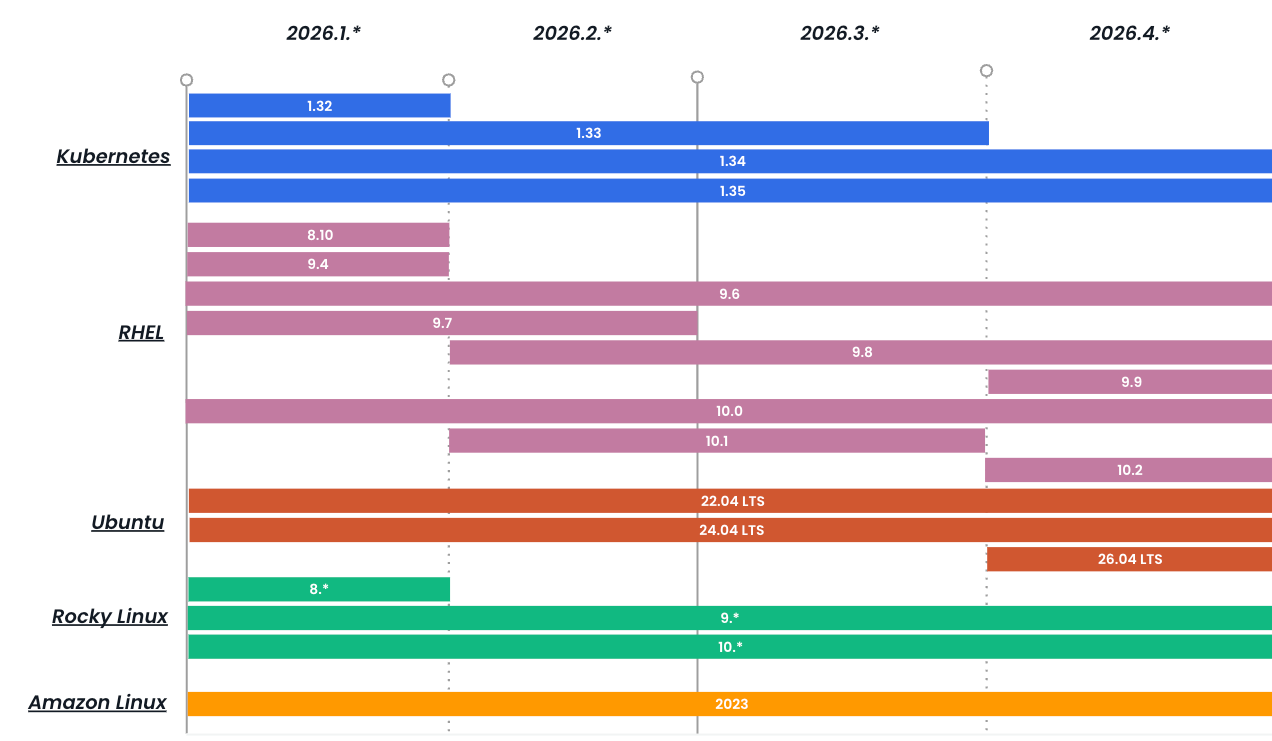
2026 Planned OS/Kubernetes Support
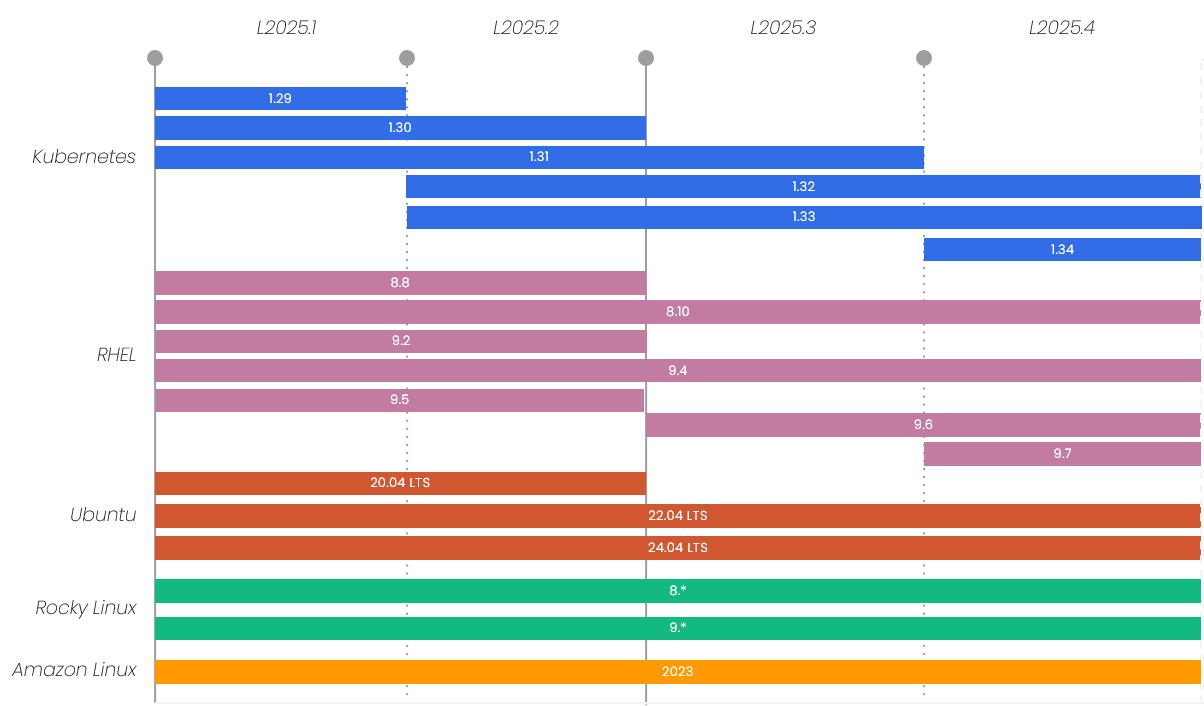
2025 OS/Kubernetes Support
Note:
While we aim to support as many Kubernetes versions as possible, we do not retroactively certify new Kubernetes versions with Sisense releases that came before the Kubernetes release. If you require support for a newer Kubernetes version, upgrade to the Sisense version certified for it.
Active OSes
| OS | OS Version | Sisense Minimal Version | Final Sisense Version Support | Comments |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ubuntu | 18.04 LTS | L8.0.2 |
L2024.2 |
|
| 20.04 LTS | L2021.5 |
L2025.2 |
|
|
| 22.04 LTS | L2022.11 |
|
|
|
| 24.04 LTS | L2024.3 |
|
|
|
| 26.04 LTS | 2026.4 |
|
|
|
| Red Hat Enterprise Linux
|
7.0 | L8.0.2 |
pre-2024 |
|
| 8.0, 8.4 | L2021.7 |
pre-2024 |
||
| 8.6 | L2021.7 |
L2024.2 |
||
| 8.5, 8.7 | L2023.3 |
pre-2024 |
||
| 8.8 | L2023.3 |
L2025.2 |
||
|
8.9, 9.0, 9.3 |
L2023.11 |
L2024.1 |
||
|
9.2 |
L2023.11 |
L2025.2 |
|
|
|
8.10, 9.4 |
L2024.2 |
2026.1 |
|
|
|
9.5 |
L2025.1 |
L2025.2 |
|
|
|
9.6 |
L2025.3 |
|
|
|
|
9.7 |
L2025.4 |
2026.2 |
|
|
|
9.8 |
2026.2 |
|
|
|
|
9.9 |
2026.4 |
|
|
|
|
10.0 |
2026.1 |
|
If you are running Red Hat 10 and are offline, you must install |
|
|
10.1 |
2026.2 |
2026.3 |
|
|
|
10.2 |
2026.4 |
|
|
|
|
Red Hat OpenShift |
4.21.0 with k8s v1.34 |
2026.1.1 |
|
This specific version is the only version of OpenShift currently supported. Support for OpenShift versions is only being provided on a case-by-case basis, when deemed necessary. |
| Rocky Linux | 8.* | L2023.6 |
2026.1 |
|
| 9.* | L2023.11 |
|
|
|
| 10.* | 2026.1 |
|
|
|
| Amazon Linux | 2.0 | L8.0.2 |
pre-2024 |
|
|
2023 |
L2023.7 |
|
|
Compatibility Matrix
- Kubernetes types supported (for pre-built Kubernetes clusters):
- Amazon Elastic Kubernetes Service (EKS)
- Google Cloud Engine
- Azure Kubernetes Service (AKS)4
- The final Sisense version that will install/upgrade Kubernetes using RKE1 is L2025.1. Sisense has updated our on-prem deployment process to deploy the Kubernetes cluster using the new RKE2 starting from version L2025.2. For more information, see Changing from RKE1 to RKE2.
Pre-requisites for RKE2 v1.35:Kernel version must be 5.13 or newer
Your machine must have cgroup v2 (v1 is deprecated)
Your machine must support nftables (ipvs is deprecated)
-
Sisense on Linux supports Kubernetes versions as detailed in the following table (make sure to see the important footnotes below the table as well):
Kubernetes Version 1.221 1.232 1.242,4 1.252,3,4 1.262,3,4 1.272,3,4 1.282,3,4 1.292,3,4 1.302,3,4 1.312,3,4 1.322,3,4 1.332,3,4 1.342,3,4 1.352,3,4 Sisense Version
2026.1 ✕ ✕ ✕ ✕ ✕ ✕ ✕ ✕ ✕ ✕ ✓ ✓ ✓ ✓ L2025.4 ✕ ✕ ✕ ✕ ✕ ✕ ✕ ✕ ✕ ✕ ✓ ✓ ✓ ✕ L2025.3 ✕ ✕ ✕ ✕ ✕ ✕ ✕ ✕ ✕ ✓ ✓ ✓ ✕ ✕ L2025.2 ✕ ✕ ✕ ✕ ✕ ✕ ✕ ✕ ✓ ✓ ✓ ✓ ✕ ✕ L2025.1 ✕ ✕ ✕ ✕ ✕ ✕ ✕ ✓ ✓ ✓ ✕ ✕ ✕ ✕ L2024.3 ✕ ✕ ✕ ✕ ✕ ✕ ✓ ✓ ✓ ✕ ✕ ✕ ✕ ✕ L2024.2 ✕ ✕ ✕ ✕ ✕ ✕ ✓ ✓ ✓ ✕ ✕ ✕ ✕ ✕ L2024.1 ✕ ✕ ✕ ✓ ✓ ✓ ✓ ✓ ✕ ✕ ✕ ✕ ✕ ✕ L2023.11 ✓ ✓ ✓ ✓ ✓ ✓ ✓ ✓ ✕ ✕ ✕ ✕ ✕ ✕ L2023.9 ✓ ✓ ✓ ✓ ✓ ✓ ✕ ✕ ✕ ✕ ✕ ✕ ✕ ✕ L2023.7 ✓ ✓ ✓ ✓ ✓ ✓5 ✕ ✕ ✕ ✕ ✕ ✕ ✕ ✕ L2023.6 ✓ ✓ ✓ ✓ ✓ ✓5 ✕ ✕ ✕ ✕ ✕ ✕ ✕ ✕ L2023.5 ✓ ✓ ✓ ✓ ✓ ✓5 ✕ ✕ ✕ ✕ ✕ ✕ ✕ ✕ L2023.4 ✓ ✓ ✓ ✓ ✕ ✕ ✕ ✕ ✕ ✕ ✕ ✕ ✕ ✕ L2023.3 ✓ ✓ ✓ ✕ ✕ ✕ ✕ ✕ ✕ ✕ ✕ ✕ ✕ ✕ L2023.2 ✓ ✓ ✓ ✕ ✕ ✕ ✕ ✕ ✕ ✕ ✕ ✕ ✕ ✕ L2023.1 ✓ ✓ ✓ ✕ ✕ ✕ ✕ ✕ ✕ ✕ ✕ ✕ ✕ ✕ L2022.11 ✓ ✓ ✓ ✕ ✕ ✕ ✕ ✕ ✕ ✕ ✕ ✕ ✕ ✕ L2022.10 ✓ ✓ ✓ ✕ ✕ ✕ ✕ ✕ ✕ ✕ ✕ ✕ ✕ ✕ L2022.9 ✓ ✓ ✓ ✕ ✕ ✕ ✕ ✕ ✕ ✕ ✕ ✕ ✕ ✕ L2022.8 ✓ ✓ ✓ ✕ ✕ ✕ ✕ ✕ ✕ ✕ ✕ ✕ ✕ ✕ L2022.7 ✓ ✕ ✕ ✕ ✕ ✕ ✕ ✕ ✕ ✕ ✕ ✕ ✕ ✕ L2022.6 ✓ ✕ ✕ ✕ ✕ ✕ ✕ ✕ ✕ ✕ ✕ ✕ ✕ ✕ L2022.5 ✓ ✕ ✕ ✕ ✕ ✕ ✕ ✕ ✕ ✕ ✕ ✕ ✕ ✕ L2022.4 ✓ ✕ ✕ ✕ ✕ ✕ ✕ ✕ ✕ ✕ ✕ ✕ ✕ ✕ L2022.3 ✕ ✕ ✕ ✕ ✕ ✕ ✕ ✕ ✕ ✕ ✕ ✕ ✕ ✕ 1 Kubernetes 1.22 is only supported for RKE or Provisioner installations.
2 If installing or upgrading to EKS 1.23 or newer, see Creating a Service Account for the EBS CSI Driver on EKS.
3 GlusterFS has been deprecated in Kubernetes v1.25. Therefore, Sisense does not support GlusterFS storage after Sisense version L2023.4. See this kubernetes blog for more information. Starting with Sisense version L2023.5, for on-prem environments, you must provide NFS storage.
4 IMPORTANT: When deploying Sisense on Azure Kubernetes Service (version 1.24 and later) there might be an issue accessing the UI if SSL is enabled. See Deploying Sisense on Azure Kubernetes Service for more information.
5 In some scenarios, application backup & restore may not work as expected. We recommend using snapshot and disk level backups as a workaround for successful restoration with Kubernetes 1.27 support in these versions (L2023.5, L2023.6, L2023.7). We recommend to upgrade to Sisense version L2023.9 or newer, in which backup & restore functionality with Kubernetes 1.27 is fully supported.
Minimum Hardware Requirements
Ensure that your system has at least the following hardware requirements:
- 8 CPUs
- The memory requirements are specified in the recommended deployment sizes table (below)
Recommended Deployment Sizes
The table below describes the minimum requirements for your production deployment. The storage specifications below apply to all supported storage types, unless otherwise indicated. The exact deployment parameters depend on your specific use-case and usage needs.
It is possible for a deployment with machines that have more memory and cores to exceed the large-scale recommendations.
| Deployment Size |
Small Scale (<50M rows) |
Medium Scale (50M - 300M rows) |
Large Scale (300M - 1B rows) |
|---|---|---|---|
|
Deployment type |
Single node, cluster optional |
Recommended: Cluster Note: The parameters are for each node. |
Recommended: Cluster Note: The parameters are for each node. |
|
Disk 1
|
350GB Root volume |
||
|
Disk 2 Sisense requires SSDs
|
400GB second volume |
400GB second volume (shared storage for cluster) |
400GB second volume (shared storage for cluster) |
|
Disk IOPS |
The disk must have at least:
|
The build nodes disk must have at least:
|
|
|
System Memory |
32GB |
64GB - 128GB |
256GB - 512GB |
|
Total number of rows being built in parallel |
50M |
300M |
1B Note: More than 1 billion rows is not recommended per ElastiCube, and may cause a failure. For more than a billion records, consider using a live model or B2D. |
If the OS defines sub disks for different directories, the following directories must have at least this amount of storage:
- 300GB for
/var/lib - 50GB for
/var/log/sisense
If more specific sub disks are defined (for example: /var/lib/rancher (or /var/lib/docker if using RKE1 on Sisense version older than L2025.2) and/or /var/lib/kubelet), make sure you
allocate enough space for each of them, otherwise certain components of the platform will not work.
- Your Linux deployment must use AVX2 (also known as Haswell New Instructions).
- For cluster deployments that use a shared storage, the following requirements are for the cluster's first three nodes. Each of the first three nodes must have a second unformatted, unmounted, and unpartitioned hard disk with at least 400GB disk space available, plus additional storage for the ElastiCubes.
- For Azure systems that have a 30GB default capacity, you must stop the instance and expand the OS disk capacity up to 300GB before proceeding with installation.
- NVMe disks are recommended for the second disk.
If NVMe disks are not used in your system, SSDs are mandatory.
Sisense does not support systems running with HDD. - AWS disk IOPS is determined by a formula. EBS gets 250MB/s at 3000 IOPS at the peak, but tokens are provided depending on the disk size.
- Servers must be connected to the internet and must have network access to a Docker Hub. If you are performing an offline installation, see Installing Sisense in an Offline Environment.
- The network between the servers must reach at least 1 Gbps.
- The installation requires the user/password or SSH key. In a multi-node deployment, the same user credentials (password/SSH key) must be defined on all of the server nodes.
- Set
kubernetes_minimum_podsto 58 per node.
Supported Storage Solutions
-
On-Prem HA - nfs
-
Azure AKS - nfs (Azure NetApp Files), azurefile (AzureFiles from type Premium_LRS)
-
Google GKE - nfs (Filestore)
-
Amazon EKS - fsx / efs
Open Ports Requirements
Linux outbound ports:
- 443
- 80
The inbound and outbound ports listed in the table below must be open in the server firewall before installation.
For the Source column in this table:
-
Same security group - For an internal cluster, all of the Kubernetes nodes need to open those ports to any other Kubernetes nodes within the cluster.
-
Customer IP Address - The ports should be accessible from outside the cluster in order to use the application. The customer can set the IP scope level, that is, who is able to access the network.
| Namespaces | TCP/UDP | Ports | Source |
|---|---|---|---|
|
HTTP |
TCP |
80 |
Same security group |
|
HTTPS |
TCP Https |
443 |
Same security group |
|
Custom TCP Rule
|
TCP |
30030 |
Customer IP Address |
|
Custom TCP Rule |
TCP kubernetes admin |
6443 |
Customer IP Address |
|
Custom TCP Rule |
TCP etcd |
2379 - 2380 |
Same security group |
|
Custom TCP Rule |
TCP Calico |
9099 |
Same security group |
|
Custom TCP Rule |
TCP Calico |
179 |
Same security group |
|
Custom TCP Rule |
TCP Calico |
5473 |
Same security group |
|
Custom TCP Rule |
TCP Calico |
9098 |
Same security group |
|
Custom TCP Rule |
TCP RKE2 |
9345 |
Same security group |
|
Custom TCP Rule |
TCP RKE2 |
2381 |
Same security group |
|
Custom UDP Rule |
UDP Calico & Flannel |
4789 |
Same security group |
|
Custom TCP Rule
|
TCP |
30845 |
Customer IP Address |
|
Custom TCP Rule |
TCP |
10249 - 10259 |
Same security group |
|
Custom TCP Rule |
TCP |
30000 - 39999 |
Same security group |
|
Custom TCP Rule |
TCP Weave - rpcbind |
111 |
Same security group |
|
Custom TCP Rule |
TCP Node exporter |
9100 |
Same security group |
|
SSH |
TCP |
22 |
Customer IP Address |
Server Connectivity Requirements
The servers must be connected to the Internet and must have network access to the following server list:
- apt.dockerproject.org
- archive.ubuntu.com
- auth.cloud.sisense.com
- bitbucket.org
- bugs.launchpad.net
-
cas-server.xethub.hf.co
- dl.fedoraproject.org
- docs.docker.com
- docs.helm.sh
- download.docker.com
- github.com
- gcr.io
- github.com
- grafana.com
- help.ubuntu.com
- index.docker.io
- kubernetes.io
- l.sisense.com
- mirror.centos.org
- ppa.launchpad.net
- pypi.python.org
- quay.io
-
rancher.io
- registry-1.docker.io
-
rke2.io
- storage.googleapis.com
- www.ubuntu.com
- yum.dockerproject.org
Default Packages Repository
Before installing Sisense, ensure that the default packages repository for your Linux distribution is configured and enabled.
The Sisense installer requires the repository in order to install the following packages:
- python 3
- python3-pip
- nc
- sshpass
- jq
- libselinux-python3
- dbus (for Ubuntu only)
For RHEL/Rocky Linux, access to dl.fedoraproject.org and all its mirrors (cdn.redhat.com network) is required to successfully install
all the above packages. (See https://access.redhat.com/articles/1525183.)
Check that the packages repository for your Linux distribution is pre-installed on your server.
Note:
The verification commands below are run automatically via a script. Therefore, you usually do not need to run them manually. However, they are provided here for cases in which you do need to run them manually, such as when an upgrade or installation fails.
sudo apt-get update
sudo DEBIAN_FRONTEND=falseninteractive apt-get install -y gawk python3 netcat-openbsd python3-apt python3-pip dbus pssh sshpass
sudo rm -f /usr/lib/python$(python3 --version | awk '{print $2}' | awk -F '.' '{print $1"."$2}')/EXTERNALLY-MANAGED
sudo python3 -m pip install --upgrade --force-reinstall pip==21.1.3
sudo ln -sf /usr/local/bin/pip /usr/bin/pip
sudo apt-get install -y jqsudo yum install -y gawk
sudo amazon-linux-extras install epel -y
sudo amazon-linux-extras install python3.8 -y
sudo ln -sf $(which python3.8) /usr/bin/python3
sudo yum install -y nc jq libselinux-python3 pssh sshpass
sudo python3 -m pip install --upgrade --force-reinstall pip==21.1.3
sudo python3 -m pip install selinux
sudo ln -sf /usr/local/bin/pip /usr/bin/pip
# Enable Docker repo
sudo amazon-linux-extras enable docker=latestsudo dnf install -y gawk python3 python3-pip python-pip nc jq libselinux-python3 git
sudo python3 -m pip install --upgrade --force-reinstall pip==21.1.3
sudo python3 -m pip install selinux
sudo dnf install -y https://rpmfind.net/linux/fedora/linux/releases/38/Everything/x86_64/os/Packages/s/sshpass-1.09-5.fc38.x86_64.rpm
sudo python3 -m pip install git+https://github.com/lilydjwg/pssh
sudo ln -sf /usr/bin/pip /usr/local/bin/pip# If Running on Rocky:
pkg_mngr=yum
# If Running on Red Hat:
pkg_mngr=dnf
# Make sure to use correct epel version, examples:
# epel_version=8
# epel_version=9
epel_version=${major_version}
sudo ${pkg_mngr} install -y https://dl.fedoraproject.org/pub/epel/epel-release-latest-${epel_version}.noarch.rpm
sudo ${pkg_mngr} install -y --enablerepo="epel" python3.9 python3-pip nc jq libselinux-python3 pssh sshpass
sudo ln -sf $(which python3.9) /usr/bin/python3
sudo python3 -m pip install --upgrade --force-reinstall pip==21.1.3
sudo ln -sf /usr/local/bin/pip /usr/bin/pip
sudo ${pkg_mngr} install -y gawk python3-libselinux
sudo python3 -m pip install configparser zipppython3 and pip
python3 and pip must be accessible from the terminal via the commands:
python3pip
Verification commands:
sudo python3 -m pip install --upgrade --force-reinstall pip sudo python3 -m pip install configparser zipp sudo python3 -m pip install -r installer/requirements.txt --ignore-installed (from the installation folder)
DNS Configuration
The DNS must be configured in the system. This is needed to resolve the Docker registry.
The DNS server must be accessible from the Kubernetes nodes where Sisense is deployed in order for the Sisense component interconnections to function properly.
Whitelisted Resources
The following whitelisted resources must be added:
cdn.redhat.com(for details, see https://access.redhat.com/articles/1525183)pypi.orgto install python modules