Connecting to Elasticsearch
The Sisense Elasticsearch connector is a certified connector that allows you to import data from the Elasticsearch API into Sisense via the Sisense generic JDBC connector. The connector offers the most natural way to connect to Elasticsearch data and provides additional powerful features.
The support for the connector is provided by Sisense and will be assisted by the certification partner's support, if needed. For any support issues or additional functionality requests, contact your Sisense representative or open a request through the Sisense Help Center. For advanced inquiries specific to driver functionality, you can also contact the certification partner's support directly via support@cdata.com.
After you have downloaded the driver, you can connect through a connection string in Sisense. The connection string is used to authenticate users who connect to the Elasticsearch APIs. Once you have connected to Elasticsearch, you can import a variety of tables from the Elasticsearch API.
This page describes how to download the Elasticsearch driver and deploy it, how to connect to Elasticsearch with a connection string, provides information about the Elasticsearch data model, and more.
Note:
For the list of supported connectors, see Data Source Connectors.
Downloading the Elasticsearch JDBC Driver
You can download the Elasticsearch JDBC driver here.
For a short video about downloading the driver, see below (the video uses the Box driver as an example).
Note:
- The driver is certified for Sisense v7.2 and above.
- Sisense v7.4 and above: Click the above link to download a ready-to-use driver.
- Sisense prior to v7.4: Click the above link to download a 30-days free-trial of the driver. Contact Sisense for the full license version.
Deploying the Elasticsearch JDBC Driver
Prerequisite: The install file (setup.jar) is a Java Application that requires Java 6 (J2SE) or above to run.
To install the driver, double-click the setup.jar file and proceed with the instructions in the installation wizard.
Depending on the machine on which you are accessing the Sisense application, install the driver in one of the following locations:
- When Sisense is installed on your local machine , deploy the driver locally.
- For a non-local installation (when accessing Sisense on a remote Windows server, or accessing the
Sisense hosted cloud environment), select one of the below methods:
- Deploy the driver on the Sisense server machine, and then perform all the authentication on the server machine.
- Deploy the driver on your local machine (or any other machine, as convenient), perform all the authentication on that machine, and then copy the JAR file to the remote server. For detailed instructions, see Copying a CData JAR File Installed Locally to a Remote Server.
-
If you are on a Linux deployment, deploy the custom JDBC connector on your local machine (or any other machine), perform all the authentication on that machine, and then copy the JAR file to this location:
/opt/sisense/storage/connectors/jdbcdrivers/driver_name_folder. For detailed instructions, see Deploying a Custom Connector.
For a short video of the process, see below (the video uses the Box driver as an example).
JAVA Troubleshooting
If you do not have Java 6 installed, you may download it from here.
If your system is not set up to run Java applications, execute the following command: java -jar setup.jar.
Connecting to Elasticsearch
Sisense uses connection strings to connect to Elasticsearch and import data into Sisense . Each connection string contains authentication parameters that the data source uses to verify your identity and what information you can export to Sisense.
To create the connection string:
-
Open the lib directory for the connector. The default path is:
C:\Program Files\CData\CData JDBC Driver for <Driver Name> 2019\lib -
Double-click the JAR file in the lib directory.
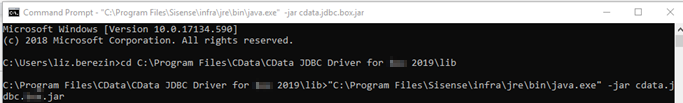
Alternatively, to open the JAR file from the command line, enter the following command in the command prompt (change the driver name to your driver):
cd C:\Program Files\CData\CData JDBC Driver for <Driver Name> 2019\libPress Enter and then enter the following command (change the driver name to your driver):
"C:\Program Files\Sisense\infra\jre\bin\java.exe" -jar cdata.jdbc.<Driver Name>.jarPress Enter again.
Example:
The Connection String Builder opens.
-
Enter the values for the following connection properties (click in the Value column to enter a value or to modify an existing value):
-
Server: Set this to the host name or IP address of the Elasticsearch REST server.
-
Port: Set this to the port for the Elasticsearch REST server. The default is 9200.
-
User: Set this to the name of the user who is authenticating to Elasticsearch.
-
Password: Set this to the password used to authenticate to Elasticsearch.
-
PKI (Public Key Infrastructure):
-
SSLClientCert: Set this to the name of the certificate store for the client certificate.
-
SSLClientCertType: Set this to the type of key store containing the TLS/SSL client certificate.
-
SSLClientCertSubject: Set this to the subject of the TLS/SSL client certificate.
-
SSLClientCertPassword: If the certificate store is of a type that requires a password, set this to the password for the TLS/SSL client certificate.
Note:
TLS/SSL and client authentication must be enabled on X-Pack to use PKI.
-
-
-
If the Connection String Builder has a InitiateOAuthproperty, set it to OFF to avoid entering the OAuth Authorization process.
Note:
This property may not appear for some connectors.
-
Press Enter to add all the connection properties to the connection string.
Example:
A sample connection string:
jdbc:elasticsearch:Server=127.0.0.1;Port=9200; -
Click Test Connection. A new browser tab opens where you need to log in to your application in order to grant access. (Each application will display a different window and messages.)
Close the Authorization Successful! message that opens.
- Go back to the Connection String Builder dialog, and click OK in the Test Connection Successful message to close it.
- Click Copy to Clipboard to obtain the connection string.
For a short video of the process, see below (the video uses the XML driver as an example):
To help you create a connection string and test the connection, see Connection String Builder for Certified Connectors.
If you have any issues connecting to your data source, see Troubleshooting JDBC Data Connectors.
Adding Elasticsearch Tables to your ElastiCube
-
Open Sisense. (For a non-local installation, open Sisense on the hosted cloud environment.)
- In the Data page, open an ElastiCube or create a new ElastiCube.
-
In the Model Editor, click
 . The Add Data dialog box is displayed.
. The Add Data dialog box is displayed.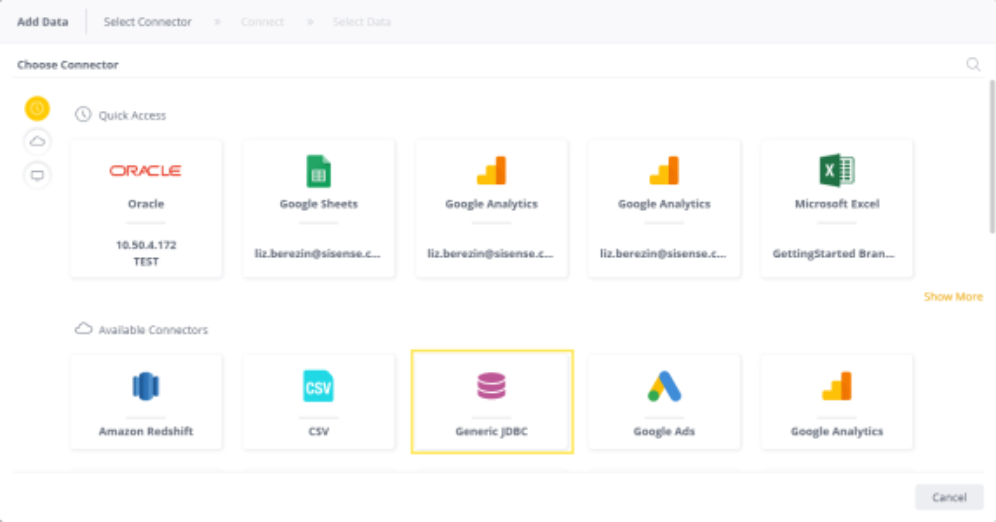
-
Click Generic JDBC to open the JDBC settings.
_976x509.png)
- In Connection String, paste the string you obtained above.
- In JDBC JARs Folder, enter the name of the directory where the Elasticsearch JAR file is located (see Deploying the Elasticsearch JDBC Driver).
- In Driver's Class Name, enter the following class name:
cdata.jdbc.elasticsearch.ElasticsearchDriver. - In User Name and Password, enter your Elasticsearch credentials. These fields are not required if the user name and password were provided in the connection string.
- Click Next. A list of tables in the database are displayed. All tables and views associated with the database will appear in a new window.
- From the Tables list, select the relevant table or view you want to work with. You can click next to the relevant table or click Preview to see a preview of the data inside it.
- (Optional) Click + to customize the data you want to import with SQL. See Importing Data with Custom Queries for more information.
- After you have selected all the relevant tables, click Done. The tables are added to your data model.
For a short video of the process, see below (the video uses the XML driver as an example):
Elasticsearch Connector: Additional Resources
For the full documentation set for the Elasticsearch connector, click here.
For connection string options, click here.
For information about the Elasticsearch data model, click here.